- Home
- Lean Principles
- Machine Selection
- Mold Design
- Mold Interlocking
- Mold Making
- Plastic Material Technology
- Molding Process
- Plastic News
- What's New
- Privacy Policy
- Disclaimer
- Site Map
- Poll
- Polishing
- 3D Rapid Prototyping
- Molding Companies
- Contact Us
- Proven Thinwall Packaging Mold Designs For Sale
- MOLD WEIGHT CALCULATOR
- HOT RUNNER VERSUS COLD RUNNER
Hot Runner versus Cold Runner in Injection Moulding
In the plastic injection molding industry, its important to know the difference between hot runner versus cold runner. Before getting into the detailed, it's essential to understand what these terms mean. Both hot runner and cold runner refer to the systems used in injection moulding machines to transfer the molten plastic from the machine's injection unit to the mould's cavities.
Discounted Mould Design For Sale
500ml Thinwall Disposable Food Tub 16.5 Grams
Difference between Hot Runner & Cold Runner
The primary difference between these two systems lies in their treatment of the plastic from the injection until it reaches the mould's cavities. In a cold runner system, the plastic is injected into the runner, which cools it down before it reaches the mould cavity. The cooled plastic is then ejected along with the part after moulding, essentially "wasting" some material.
In contrast, a hot runner system features an electrically heated manifold that maintains the plastic in a molten state, all the way from the injection unit to the mould cavities. The advantage here is that there's no solid plastic runner ejected after moulding because the material inside the runner stays molten.
The cold runner system has been in use for a longer period and is known for its simplicity. One of the advantages of a cold runner system is its simplicity in mould making. Cold runner moulds have fewer components and are less complex and cheaper to make and maintain.
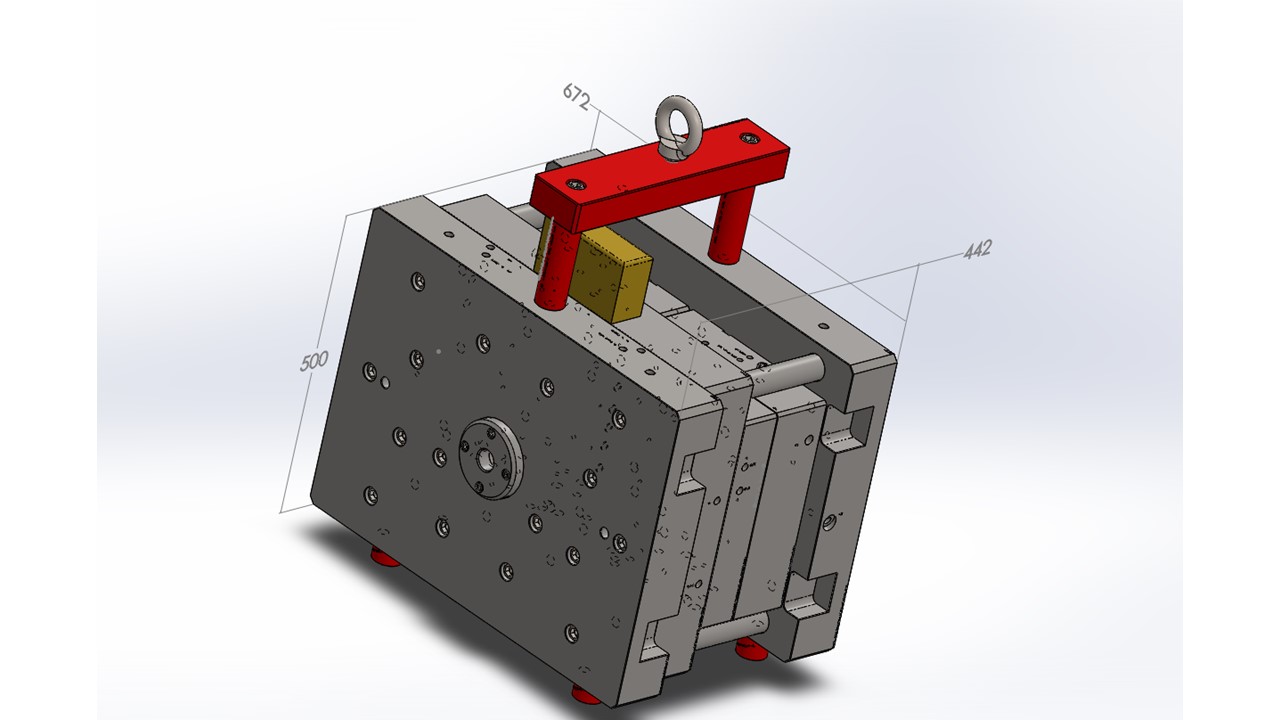
 HOT RUNNER 2 CAVITY
HOT RUNNER 2 CAVITYAdvantages/Disadvantages
However, cold runner systems can present several challenges. Firstly, the material wastage factor is higher as the runner is solidified and ejected with each moulding cycle. Further, this waste material needs to be reground, which can result in a decrease in material properties and overall part quality.
In addition to the waste issue, a cold runner system may also increase cycle time. Since the plastic in the runner needs time to solidify, the overall cycle time may increase. More cooling time indicates longer cycle times, which can reduce production efficiency.
Regarding hot runner systems, one of their biggest advantages is the significant reduction in material waste. Since the runner system remains hot, the plastic does not solidify. Not only does this eliminate waste, but it also leads to a continuous flow of plastic, which simplifies the moulding process.
Hot runner systems also offer a boost in production speed. By maintaining the plastic in a molten state, the cycle times get reduced. Shorter cycle times mean more parts are produced per hour, improving production efficiency.
However, hot runner systems are not without their challenges. The foremost being the initial investment cost, as setting up a hot runner system can be quite expensive due to the complex components involved.
Another potential issue with hot runner systems is the difficulty and cost associated with maintenance. If a hot runner system fails, it can cause significant downtime, as repairing the system can require a lengthy shutdown of the injection moulding machine.
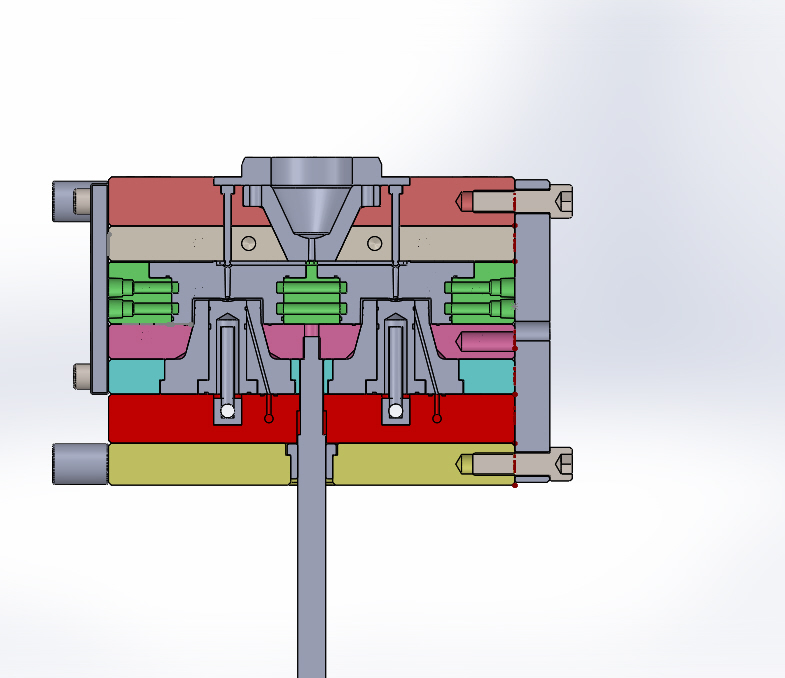
 COLD RUNNER 2 CAVITY
COLD RUNNER 2 CAVITYWhen to use hot runner versus cold runner
Determining whether to use a hot runner or cold runner system depends on several factors, including the production volume, part design, material selection, and overall budget. For instance, a high-production-rate part might be best suited for a hot runner system to minimize waste and maximize efficiency.
On the other hand, if initial cost is a primary concern and production volumes are low, a cold runner system might be the best option. Paying for a hot runner system might not be worth the investment for short-run parts or prototypes.
When it comes to part design, some complex designs require the use of hot runner systems. Hot runners allow for balanced fill, leading to more consistent part quality and limiting the need for secondary operations.
Equally, certain materials may be more suited to one system over the other. Some materials won't perform well in a hot runner system, while others will degrade if regrinding is required in a cold runner system.
Even though hot runner system might seem expensive initially, in the long run, they might lead to cost savings. The savings come from reduced cycle time, less material waste, and lower labor costs.
Conversely, while the cold runner system might be cheaper upfront, over time, costs can add up due to waste material, longer cycle times, and other factors. Therefore, long-term cost considerations should play a significant role when deciding between hot runner and cold runner systems.
Hence, in the debate between hot runner versus cold runner systems, it is essential to consider all these factors mentioned above. There's no one-size-fits-all solution, and the choice will depend on multiple aspects including the project's unique requirements and objectives.
Conclusion Hot Runner versus Cold Runner
To summarize, understanding the advantages and challenges of both hot runner and cold runner systems will enable better decisions when selecting which method to use for injection moulding. While both systems have important roles to play, the most effective choice will vary depending on the project's specific needs and objectives, making it crucial for practitioners to fully grasp each system's operation and potential benefits. With the right choice, the plastic injection molding process can start saving you money immediately, by harnessing the potential of these systems to their fullest.