- Home
- Lean Principles
- Machine Selection
- Mold Design
- Mold Interlocking
- Mold Making
- Plastic Material Technology
- Molding Process
- Plastic News
- What's New
- Privacy Policy
- Disclaimer
- Site Map
- Poll
- Polishing
- 3D Rapid Prototyping
- Molding Companies
- Contact Us
- Proven Thinwall Packaging Mold Designs For Sale
- MOLD WEIGHT CALCULATOR
- HOT RUNNER VERSUS COLD RUNNER
Plastic Injection Molding Machine Selection – Why It Is Important
Selecting the right plastic injection molding machine is one of the most important criteria in making quality parts consistently and profitably. The right machine will help keep costs low and make you more competitive. This will allow you to sell more parts, earn more money and at the same time establish a reputation as a quality manufacturer.
Even better, you will have the security of long term customers.
Discounted Mould Design For Sale
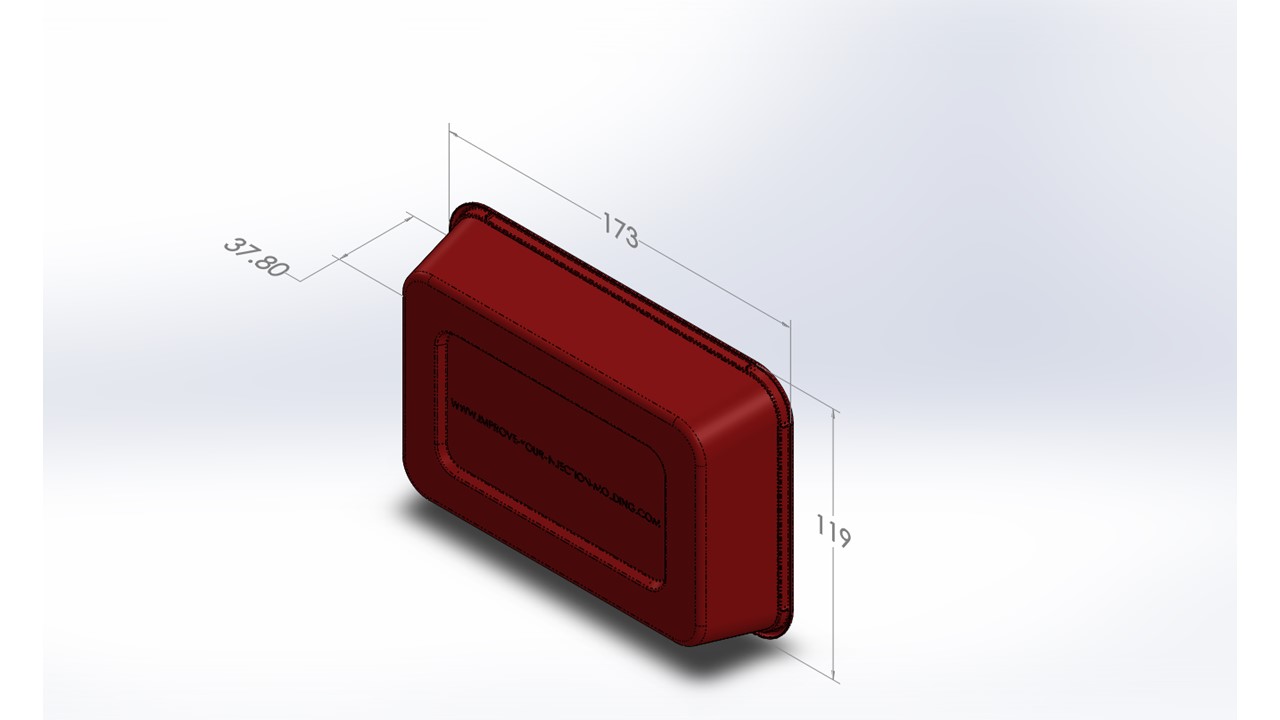
500ml Thinwall Disposable Food Tub 16.5 Grams
How To Keep Your Costs Low:
- Minimize reject rate (set a target <1%) Click here to read about how to eliminate warpage quality issues.
- Reduce energy consumption of all injection molding machines
- Have faster cycle times
- Eliminate unscheduled machine downtime –(no breakdowns)
A properly selected plastic injection molding machine will give you all of the above.

Common Machine Selection Mistakes And Their Consequences
The best way to appreciate the importance of correct plastic injection molding machine selection is to list the most common mistakes made when selecting machines and the effect on part quality and productivity.
Mistake #1
Buying Used Injection Molding Machines That Don't Work
The key to buying a reliable used machine is to find one that has been fully inspected and tested before delivery so that you won’t suffer loss of production due to multiple breakdowns.
Click here to see a case study of how incorrect machine selection can effect part quality Example #2).(opens in a new window)
Mistake #2
Selecting Large Screw Diameters.
Large screw diameters can cause quality problems due to material degradation. When small shot sizes are used with large screw diameters, the plastic material spends more time being heated by the barrel heaters compared to large shot sizes. Material degradation is more likely to occur if the shot size is small compared to the injections units maximum shot capacity especially for heat sensitive materials.
Another problem with large screw diameters are the large shearing forces generated during screw rotation, this can also degrade the material and is likely to lead to reject parts.
Mistake #3
General Purpose Screws
The advantage of a general purpose screw is that they can be used with most plastic materials such as PP, PE, Nylon, PET and PC so they are very flexible and good for moulding companies that mould a variety of different materials.
The disadvantage is that, for some materials, part quality and productivity rates will be lower compared to more advanced injection molding screw designs such as the barrier screw. Click here to learn more about screw selection.
Mistake #4
Injection Pressure Limited.
To consistently make quality parts the molding process must not be limited by the injection pressure. It is advisable to have at least 10% injection pressure in reserve so that the injection molding machine can automatically adjust to normal variation in the plastic material viscosity.
Insufficient injection pressure will produce short moldings.
The injection units screw diameter governs the available maximum injection pressure so it is critical to choose the correct diameter when buying a plastic injection molding machine.
Mistake #5
Inadequate Clamp Tonnage
If clamp tonnage is too low then it will be difficult to produce quality parts. Low clamp tonnage means inconsistent weights, flash, short shots, wall section variation, poor surface finish and size variation.
Machine and mold wear will be excessive.
Mistake #6
High Energy Consumption
Have you ever noticed how there is almost no difference in your cars fuel consumption with 2 people in it compared to just 1 person? A moulding machine is the same. A small mold will require almost as much energy to open and close the platen compared with a medium size mold. A properly selected plastic injection molding machine will use power very efficiently.Click here to learn about how to reduce your energy bill on your existing machinery by changing parameters in the plastic injection molding process.
The type of machine design also plays a significant role in power consumption. There are 3 types of machine designs: fully hydraulic, fully electric and hybrid machines. Hybrid machines are partly electric and partly hydraulically operated. Selection largely depends upon the type and quantity of parts to be molded.
Plastic Injection Molding Machine Selection Process
1. Know the plastic parts you intend to mold
2. Select machine type: Hydraulic, hybrid or electric
3. Calculate clamp tonnage requirements
4. Calculate the injection unit size.
1.Know The Plastic Parts You Intend To Mold
The process of selecting the right machine starts with knowing the particular plastic parts that will be moulded by the machine. Molding parts that are not suited to the machine will result in frustration with on-going quality problems, slow cycle times and machine and mold damage.
If you are planning to buy Cap or Closure Molds then click here to get a quick mold quote from a reputable mold maker. (Opens in a new window)
You should know the part:
- Plastic material
- Weight
- Length x width x height
- Average wall section
- Gate location
- Maximum flow length from the gate
- Estimated cycle time. Click here to estimate cycle time.
- Quality requirements
- Annual quantity requirements. Click here to get to the production calculators used for scheduling.
In addition you should also know the mould size and weight.The correct part information will then allow you to find the injection unit size, clamp tonnage requirements and machine type.
2.Select Machine Type
Types of plastic injection molding machine designs available:
- Fully Hydraulic
- Fully Electric
- Hybrid - combination of hydraulic and electric drive
Fully Hydraulic Machines
The types of hydraulic machines available are defined by the type of clamp design, type of hydraulic pump design and the presence or absence of an accumulator.
Clamp design is either a toggle clamp or by hydraulic ram.
Hydraulic pump design can be a constant displacement pump (also called fixed displacement pump), a variable displacement pump (also called a piston pump) or a servo pump (also called frequency control or RPM control) .
If an accumulator is present then some machine manufacturers use it to drive the entire machine, while others use it for the injection stage only. Accumulators are required for molding of parts which have wall thicknesses in the range of 0.3mm to 0.8mm – this is known as thin wall molding.
Accumulators might also be required for moulding thicker parts but this must be checked on a case by case basis.
Which one is suitable for you?
It depends on your priorities.
Here are some criteria to consider before selecting a hydraulic moulding machine:
- Buy a new or used machine
- Purchase price
- Energy efficiency
- Plastic material to be processed
- Part design
- Mould design
- Clean room requirement
- Cycle time requirement
- Hold time requirement
- Local service agent capability
If low power consumption is a priority then choose a hydraulic machine with a servo pump as this is the most energy efficient of the fully hydraulic machines. A servo pump will only operate when the machine requires movement, the rest of the time it is using minimal power. However, the purchase price is 10%-15% higher than a hydraulic machine with a constant displacement pump or even a variable displacement pump.
Keep in mind a servo pump control will only save you power if you have long cooling times or machine inactive times such as long take out time for robot.
Fully Electric Plastic Injection Molding Machines
Every movement of the machine is done with direct drive electric servo motors only drawing power when movement is required so they are very energy efficient. Electric machines have excellent repeatability which virtually guarantees consistent part quality. This makes them suitable for molding medical devices. Click here to learn more about medical injection molding.
Electric machines are suited to clean room operations because there is no hydraulic oil that can leak on to the floor. Click here to learn more about electric molding machines.
Hybrid Plastic Injection Molding Machines
A hybrid plastic injection molding machine uses a combination of hydraulic drive and electric direct drive. The hydraulic drive is used to generate fast injection speeds when moulding thin wall parts. The rest of the machine uses electric drive servo motors and each axis of the machine has its own dedicated motor. For example, the mould opening/closing stroke has its own motor.
These injection molding machines are very energy efficient
3.Calculate Clamp Tonnage Requirements
Clamp tonnage requirements for your plastic injection molding machine can be calculated by:
- By experience – injection molders and machine manufactures have this information
- Computer simulation software (Click here to learn more about the benefits of using simulation software.)
- As a rough guide, a simple calculation Projected Area X Average Cavity Pressure X Number of Cavities. (Click here to find the machine clamp tonnage for plastic parts made from polypropylene).
In order to find the tonnage using the simple calculation the following part information is required:
- Plastic material
- Length x width x height
- Projected area (length X width)
- Average wall section
- Gate position
- Maximum flow length from the gate
- Number of cavities in the mold
The average cavity pressure is also required and this information is available in some plastic injection molding machine manufacturers hand book for certain materials.
Most injection molded parts average cavity pressures lie in the range of 300-800 bar. Parts with long flow paths and thin walls will have pressures in the upper range while parts with short flow lengths and thicker wall sections will have much lower pressures.
Plastic material selection also influences the cavity pressure.
In addition, you need to know the mold weight and size so that you can check that the mold will physically fit into the machine and that the machine can carry the mould weight. Click here to learn about our mold design services.

4.Calculate The Injection Unit Size
To select the right unit for your plastic injection molding machine you must know part:
- Plastic material
- Cycle time
- Cooling time
- Shot weight (part weight, cold runner weight and number of cavities)
- Peak injection pressure requirement
- Plasticizing rate
- Injection rate
- Hold time and pressure
For a specific tonnage machine, manufacturers usually offer 2 injection units to choose from. Both units usually have 3 different screw and barrel assemblies on offer. In order to select the correct assembly, the shot size must be calculated as a percentage of the injection capacity and must lie between 25% and 65% so that good quality parts can be made.
Most screw and barrel assemblies are rated in grams of general purpose polystyrene (GPPS). To calculate the shot capacity for materials other than for GPPS the melt density needs to be known.
Lets assume we have a screw and barrel assembly with a screw diameter of 56mm and the capacity is 510 grams of GPPS. What is the injection capacity for polypropylene (PP)?
Assume melt density of GPPS = 0.945 grams per cubic centremeter
and melt density of Polypropylene = 0.74 grams per cubic centremeter
(Be sure to use melt density & not room temperature density for this calculation)
Calculation to find injection capacity for PP:
(Density of PP/Density of GPPS)xBarrel capacity of GPPS grams
=(0.74/0.945)x510 grams=399 grams PP
So maximum injection capacity of PP for this 56mm screw diameter is 399 grams.
Next we need to make sure the shot size is within the maximum and minimum limits of between 25% and 65%.
If the shot size for the injection mould is 110 grams (includes cold runner) then the shot size as a proportion of the total injection capacity is:
=(110/399)x100= 28%
which is within limits.
Click here to get to the Injection Capacity Calculator (opens in a new page).
Next, the following 3 criteria must be confirmed to be within limits of the injection unit with the 56mm diameter screw.
- Injection pressure
- Plasticizing rate
- Injection rate
These can be found in one of 2 ways:
The first is by experience - perhaps you have a similar part in production in which case you can read the pressure directly off the screen. Be sure to check the screw diameter is the same.
The second is by computer simulation but keep in mind the results are only as good as the information that is entered. It is advisable to check these results against some real life examples.
Just remember, the screw diameter selected is crucial to long term part quality and productivity.
Return from Plastic Injection Molding Machine Selection to Home Page